Study on the Design of Water Treatment Scheme for Expressway Tunnel in a Mountainous Area- Juniper Publishers
Civil Engineering Research Journal- Juniper Publishers
Abstract
In the process of tunnel construction in karst area, unexpected geological disasters such as water inrush and mud inrush are often encountered, which brings great disaster and incalculable economic loss to the construction safety, in order to ensure the smooth operation of tunnel construction and the safety of the late construction of the tunnel, it is necessary to select and remove the reasonable construction plan. In the course of highway tunnel construction in a mountainous area, after entering the rainy season, with the tunnel digging into the melting section of the Xeon Rock, the tunnel water inrush and seepage are obviously aggravated, and after the natural drainage of the original design is serious, the reason of the water accumulation in the hole is analyzed, three kinds of water treatment schemes in the hole are formulated, The best treatment scheme was eventually selected. It provides reference for similar karst groundwater treatment and tunnel construction scheme design.
Keywords: Mountain highway tunnel; karst treatment; Scheme design
Introduction
Karst distribution in China is very extensive, accounting for about 1/3 of the land area, karst phenomenon throughout a number of provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities, especially in the southwest Region [1]. With the rapid development of hydropower construction in China, with the introduction and implementation of the National Strategy for the development of the western region, tunnel construction plays an important role in the transportation system, and tunnel inrush water is the most prominent geological disaster in the process of tunnel construction. In the tunnel construction often encounter water inrush, gushing mud and other geological disasters, seriously affect the construction safety, the tunnel construction and operation is also extremely unfavorable [2]. Based on the concrete project case, this paper introduces the comparison between the drainage method of water accumulation problem and the application problem of hydraulic control method in the construction of tunnel under karst geological conditions [3,4], and the best governance plan was selected in the context of various factors.
Project Overview
The tunnel is located in Liupanshui, Guizhou Province, and the route crosses the middle and Low mountain Watershed zone between Yuexi and Jinggou; The tunnel is separated from the double line, the left-line tunnel is length 3772m, the right-line tunnel length 3800m, is the extralong tunnel; The tunnel profile adopts unidirectional slope, the tunnel route area is located in the subtropical monsoon humid climate ,the climate is pleasant, the tunnel is built in the lava area wiring, the bad geology in the area is mainly karst, in the range of seasonal variation zone of the main body of the tunnel hole, the underground karst is extremely developed, the infiltration condition is good, the groundwater runoff path is short, the water inrush in the rainy season is large, the surface dissolution depression, the funnel and so Gravel and other substances, the rainy season is a surface water collection area.
Tunnel from the beginning of construction, the early construction of the tunnel is relatively normal, the total water inrush in the exit section is generally around 2500 m3/d, the import section using natural smooth slope drainage, water inrush under normal circumstances 1200 m3/d (estimate). Since entering the rainy season, with the excavation of the tunnel outlet section into the melting section of the Xeon Rock, the tunnel water inrush, seepage significantly intensified, water inrush gathered in the vicinity of the tunnel palm, resulting in the cavern was submerged, construction blocked. In order to better solve the problem of tunnel water accumulation, supplement the special hydrogeological survey work, use comprehensive survey means to further explore the hydrogeological and engineering geology of the tunnel, and provide more detailed hydrogeological basis for the treatment of karst groundwater and the tunnel construction scheme.
Cause analysis of tunnel water accumulation
The effluent point of karst fractured water in tunnel is mainly concentrated in the effluent from the exposed karst pipeline effluent and the karst fractured water concentrated effluent passage. The dissolving cavity has a certain discharge capacity, according to the existing several heavy rainfall tunnel water accumulation situation found that the original karst pipeline has a good discharge capacity [5-7], but with the pipeline construction water and tunnel water discharge, karst pipeline discharge capacity has been greatly affected, or even blocked, in the case of heavy rainfall, The occurrence of groundwater reflux into the tunnel in the Karst pipeline. In the concentrated effluent section of karst fractured water, the lower seepage of karst fractured water in this section is slow, and the groundwater in the area after heavy rainfall is a short and sharp increase, and the original design uses encrypted annular and transverse drainage measures to reduce the head pressure behind the lining in order to ensure the safety of the tunnel structure, However, judging from the cracking of seepage in lining after several recent heavy rainfall, the groundwater diversion measures behind the lining are not very effective. A summary analysis of the main causes of water accumulation in the hole:
i. The drainage capacity of the dissolving cavity drain channel is insufficient, and the construction drainage causes the dissolving cavity blockage;
ii. In the case of heavy rainfall, groundwater infiltration is too large to exceed drainage capacity
iii. The discharge capacity of karst fractured underwater seepage channel is low, and the groundwater level rises sharply under the condition of heavy rainfall.
Design of treatment scheme for tunnel water accumulation
Due to the construction of a large number of tunnels in karst area, tunnel workers have mastered some construction treatment techniques and successful experiences in karst areas. Junhua Zai [8] Quansan expressway Sanyang tunnel large inrush water treatment, put forward the combination of plugging, plugging mainly treatment measures; Lihui Nan [9] It is suggested that when seasonal rainfall is strong, when the effect of grouting water plugging is not particularly good, then the drainage pressure is used to drain and buck, and when the displacement of the spillway hole does not meet the requirements, the drainage capacity can be improved by adding transverse drainage channel and drain hole; Qiangqiang Cheng [10] A reinforcement technique of top-down segmented grouting is used to deal with water inrush in a large team through waterwaterrich karst strata. The monitoring results show that the grouting reinforcement technique has good effect, overcomes the defect of repeated sweep hole greatly improves the construction efficiency, and saves the construction time; Xiaocheng Liu [11] An analysis of the present situation of groundwater treatment research in tunnel construction the paper puts forward that “plugging combination” is the basic method to control the groundwater problem in tunnel construction; Zhenhua Fang [12]In the study of the disease of Karst pipeline inrush in the Alpine Tunnel on the Chenggui Railway, an additional spillway hole scheme was proposed to rectify the water inrush disease; Jing Li, et al. [13] The large karst water inrush disease appearing in the Guanhuchong Tunnel is designed for how to deal with the large amount of water inrush in the cavern safely and effectively; Xinguo Du [14] In the process of karst water treatment in Makoupai tunnel, the dynamic optimization design is carried out, and the final control construction scheme is obtained. Roughly divided into two aspects, one is to deal with Karst, the other is to adjust the tunnel Construction methods ; the treatment of inrush water, follow the “sparse mainly, plug and discharge combination, local conditions, comprehensive management” principle, as far as possible not to change the seepage path of water, according to the actual situation to choose to Drainage or blocking mainly, At the same time, consideration should be given to the minimum impact of the measures taken on the hydrogeological conditions and surrounding environment of the tunnel . The design of the treatment scheme of karst water is mainly considered from two aspects of tunnel drainage capacity problem and tunnel structure safety, on the one hand, the discharge of groundwater under the condition of heavy rainfall. The existing tunnel drainage system cannot fully meet the requirements of karst fractured water discharge after considering the pipe trench siltation and other factors, so there are two kinds of schemes to increase drainage capacity and reduce karst fractured water discharge in the treatment scheme. On the other hand, the safety problem of tunnel structure is divided into the safety of tunnel lining structure and the stability of tunnel base. In view of the above situation, the treatment measures of are worked out: Based on the above analysis, three treatment schemes are proposed.
Scheme I
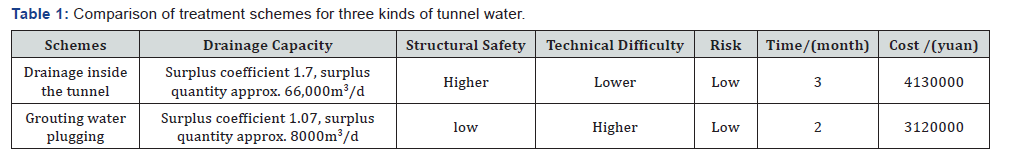
Drainage inside the tunnel, the tunnel on both sides of the road to add drainage dark Ditch, the cavern reserved Cable trench Drainage pipe interface, left and right hole center ditch co-deployment drainage, karst fracture section lining foot added transverse guide water pipe. According to hydrogeological data, the maximum effluent capacity of tunnel single hole is 98420m3/d, and the total drainage capacity of the inner drainage scheme is estimated, in which the left and right hole coordinated drainage is calculated according to 15000m3/d, and the total drainage capacity of the cavern drainage scheme considering siltation and other unfavorable factors is about 166939m3/d, drainage capacity is 1.7times the forecast water inrush. The residual coefficient of drainage capacity corresponding to the remaining displacement of the right hole is 1.92, the surplus coefficient of drainage capacity of two holes is higher, and the drainage safety is more abundant. In terms of structural safety, a transverse water guide with a longitudinal spacing of 5m and a length of 4m is set up in the paragraph of Karst fractured water development, which can effectively reduce the underwater pressure behind the lining, and according to the existing design data Figure 1, the lining is guaranteed when the structure safety is not more than 15m (design elevation ) under the action of head pressure.
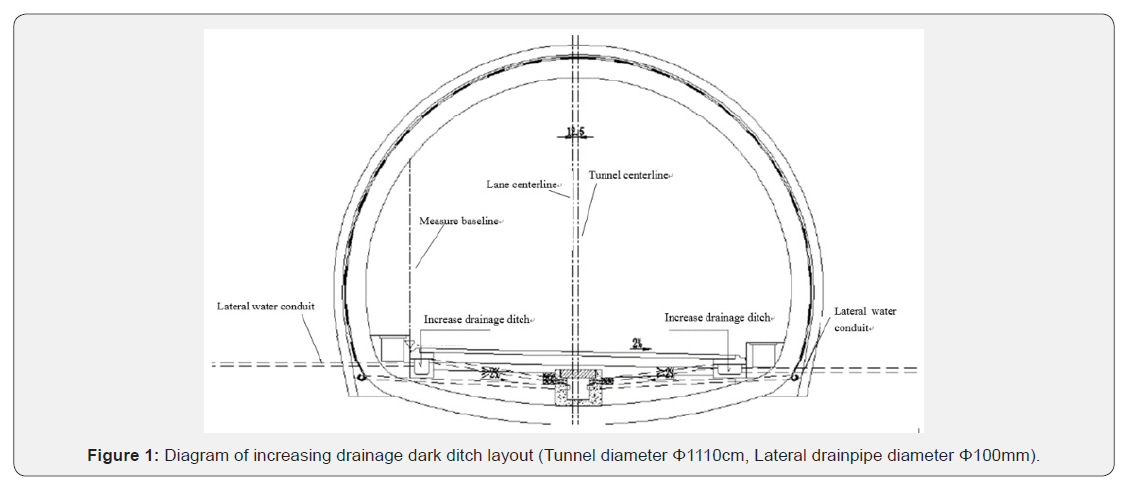
Schemes II
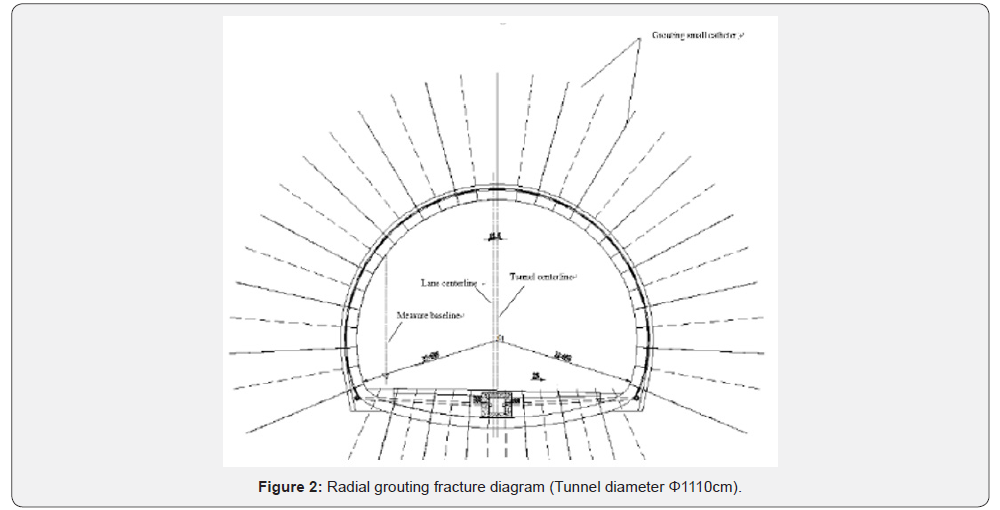
Grouting water plugging, rock-soluble fracture section lining behind the surrounding rock grouting water plugging. Grouting water plugging, through the surrounding rock grouting water plugging to reduce the amount of groundwater discharged into the tunnel. Because the data of karst fractured water effluent is not accurately obtained, it is estimated that the water inrush when the palmar surface is revealed during the construction process, according to the construction data, when the karst is exposed, the tunnel is flooded for about 200m, and the water is converted to 3360m3, according to 3 times the magnification is considered to obtain the water output is 10080m3/d, then the drainage capacity after plugging is 1.07 times , the drainage surplus capacity is small. In terms of structural safety, after grouting water plugging, the discharge of groundwater in the mountain is reduced, the water level in the interior of the rock mass will be higher, and the water pressure in the block has a great influence on the safety of two lining structures, Figure 2 resulting in local structural damage and leakage, In general, the safety of the structure is guaranteed by using the reinforced anti-hydraulic lining structure in the fully enclosed lining design of grouting water plugging.
Comparison and selection of tunnel water treatment scheme
The comparison of the scheme is mainly considered from the aspects of drainage capacity, structural safety, technical difficulty, construction risk, duration and project cost, in order to select the relative optimal scheme.
Scheme I: Drainage scheme in the tunnel
Advantages: Drainage system are located in the tunnel, construction management and quality control is simple, construction technology difficulty and construction risk are low.
Disadvantages:
a. The maintenance requirements of the drainage system in the tunnel are high, the central ditch in the tunnel, the drainage dark ditch on both sides of the roadbed and the contact channel between them are prone to siltation or even blockage, which will reduce the drainage capacity of the tunnel and have a great influence on the safety of the tunnel structure, so the regular maintenance requirements of the drainage system are high.
b. On both sides of the road drainage dark ditch cover into the road lane about 10cm, although the longitudinal length of 10m of a longer plate cover to improve the stability of the cover plate, but the slow lane heavy vehicle driving process will still have a certain impact on the road surface, when the cover plate and dark ditch side wall construction quality control is poor, The operation stage is easy to cause local damage of pavement.
c. It is necessary to carry out large section of pavement concrete side ditch excavation and part of the bottom backfill layer to break the construction, the construction efficiency is low, the main hole excavation has a certain interference.
d. When there are extreme conditions such as siltation and blockage of drainage system, the amount of short-term heavy rainfall may cause the water inrush in the hole to be discharged in time, and the road surface will be damaged by the accident.
Scheme II: Grouting water plugging
Advantages: Radial grouting consolidation can effectively improve the surrounding rock, and the formation of waterstopping ring can reduce the influence of groundwater on the stress of tunnel structure to a certain extent; The cost of treatment is relatively low.
Disadvantages:
I. Grouting Sealing construction technology is more difficult, plugging effect and construction level is closely related, it is necessary to have a wealth of grouting construction experience team to ensure the construction quality, and karst pipeline water plugging is difficult, easy to form a high pressure in the local situation, the two-lining structure of the force has a greater safety hazard.
II. The grouting holes formed by punching grouting on the two lining have been destroyed, which can destroy the lining structure and waterproof plate, and easily form local leakage.
III. Treatment paragraph two lining has been completed, two-lining drilling grouting affects the appearance of quality, the tunnel quality assessment has a certain impact.
IV. After plugging, the remaining passages still have karst fissure water pouring into the tunnel, the reduction of water inrush in the tunnel after plugging is not obvious, and the surplus degree of drainage safety is not easy to be evaluated.
Comprehensive comparison
According to the above discussion and comparison, the treatment effect of the scheme II is uncertain, the drainage surplus coefficient is low. The scheme I is designed with the maximum projected water consumption in the tunnel of 98000 m3/d, the data are estimated on the basis of 6 hours of rainfall during construction, the design basis is sufficient, the design drainage capacity is 1.7 times the maximum projected water inrush, the surplus is higher, the reliability is better, Although the scheme has some interference to the main hole excavation construction, the side gutter cover into the lane 10cm may cause the pavement to be partially damaged in the operation process, the drainage system maintenance requirements are high, but the design basis of the scheme is adequate, the drainage surplus is appropriate Table 1, the structure safety is high, the construction period basically meets the requirements, the cost is relatively lower, Therefore, it is recommended to adopt the scheme I as the treatment scheme of karst water in this tunnel.
Conclusion
The selection of construction schemes in engineering construction is particularly important. A scientific and rational construction plan will not only improve the economic benefits of project management, but also have a huge impact on the social benefits of the project. When selecting a construction plan, it is required to do a comprehensive comparison and comprehensive consideration of the actual situation of the combined project, and to find an optimal solution that can solve the engineering problem and save the engineering cost. This paper first analyzes the specific causes of water accumulation in the cave, gives a variety of treatment options, introduces the advantages and disadvantages of the treatment schemes in the water treatment in the tunnel and the matters that should be paid attention to during the comparison and selection process. The good governance program provides reference for tunnel engineering design, construction and comprehensive rectification work of similar projects.
Acknowledgements
This work is sponsored by the Found of Institute of Highway Science, Ministry of Transport (201733) and the Youth Fund of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology (20153014) which are gratefully acknowledged.
For more open access journals, please click on: Juniper Publishers
For more civil Engineering articles, please click on Civil Engineering Research Journal
https://juniperpublishers.com/cerj/CERJ.MS.ID.555749.php



Comments
Post a Comment